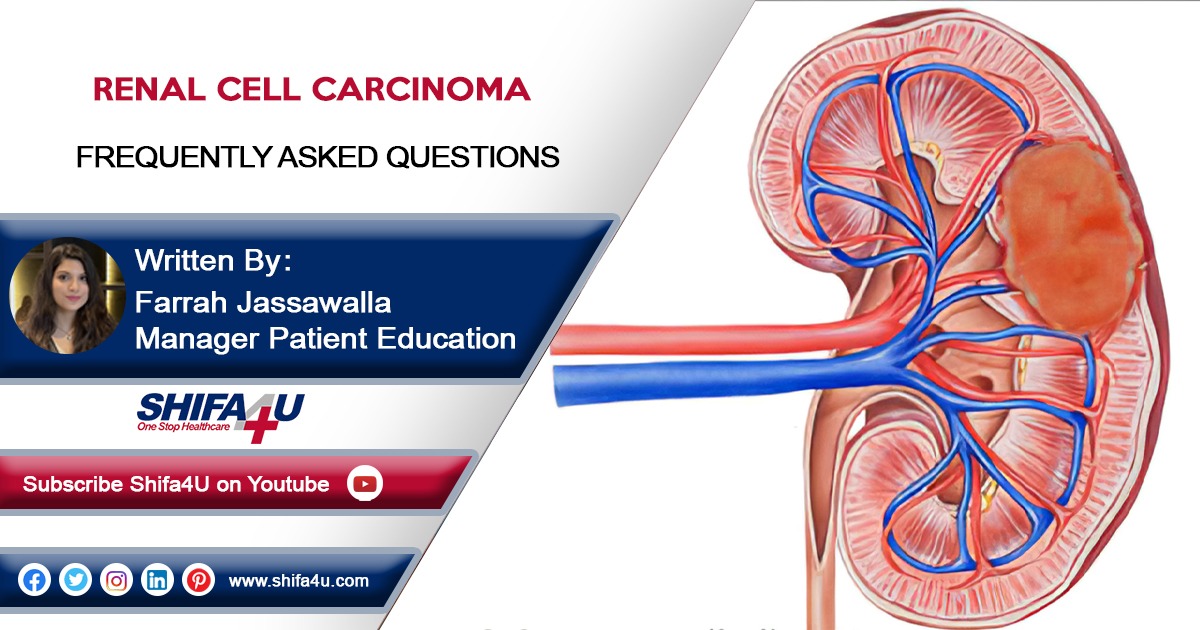


Renal Cell Carcinoma is the most common type of cancer found in the renal system or the kidneys. Kidneys are present on both sides of the backbone and help regulate and balance fluids in our body. They contain little tubes called tubules, which help in purifying blood, extracting waste, and producing urine.
RCC (Renal Cell Carcinoma) occurs when cancer cells start spreading in the kidney walls and tubules. RCC is a malignant cancer that can spread quickly to other organs of the body, like the lungs, through the blood and lymphatic system. Therefore, it must be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
The exact cause of Renal Cell Carcinoma is still not known. However, it is demographically more common amongst men between the ages of 50 to 70. Doctors believe that the following are a few of the things that increase the risk of Renal Cell Cancer in people:
● Having a family history of RCC
● Smoking
● Using drugs or overdosing on certain drugs and steroids
● Obesity and diabetes
● Having cysts in the kidney
● Hypertension
● Kidney transplant or dialysis
There are various signs and symptoms of Renal Cell Cancer, and they change as the disease grows. Some of the common symptoms are mentioned below:
● Blood in the urine
● Lump in the abdominal area or at the side
● Constant pain in the back or on one side
● Fatigue and fever
● Loss of appetite and weight loss
● Paleness and anemia
If anyone experiences more than 3 symptoms at the same time, they should immediately consult a doctor.
Doctors can suspect that a patient has renal cell cancer by noticing the symptoms and taking into consideration the patient’s family history. They conduct different tests to diagnose this cancer. Some of them are as follows:
During this test, a small piece of the tissue from the Kidney tumors is extracted. The tissue is extracted with the help of a needle that is inserted into the cyst or tumor. The tissue is then sent to the lab for examination to confirm whether the cyst is cancerous or not.
During these tests, detailed images of the kidney and its insides are produced to detect signs of cancers or tumors.
Urine samples are taken for examination in the laboratory and tested for protein, red blood cells, white blood cells and sugar levels.
To check which kind of substances are being released in the bloodstream by different organs and to check if the levels of these substances are normal or not.
After the diagnosis of renal cell cancer, tests are done to figure out the stage of cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body, like the lungs.
There are various treatments and procedures done to treat Renal cell cancer depending upon the stage of cancer and urgency of treatment. For detailed information, book an online appointment with Shifa4U. The most common treatments that a doctor might recommend are:
The patient is subjected to X-rays to kill cancer cells in the kidney. This radiation can be given externally by a machine or internally by inserting a seed or a device.
In this treatment, the cancer cells are killed by inserting drugs orally or intravenously. It is also the most common treatment for most kinds of cancer
Surgery is done at a later stage of cancer, where a part of the kidney that is affected or the entire kidney is removed. In case of removal of both kidneys, a kidney transplant is required.

Farah Jassawalla is a graduate of the Lahore School of Economics. She is also a writer, and healthcare enthusiast, having closely observed case studies while working with Lahore's thriving general physicians at their clinics.

| Lab | Original Price | Your Price | Order |
|---|
| Vendor | Original Price | Your Price | Order |
|---|
Has been successfully added in your current order.
Dr Rizwan Uppal, the founder of IDC, believed that proper and timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. An all under one roof diagnostic service with the name of Islamabad Diagnostic Center (IDC) Pvt. Ltd was established in the beautiful City of Islamabad more than a decade ago.
This brain child of Dr Rizwan was not possible without the support of his two brothers and Executive directors, Dr Rehan Uppal and Dr Imran Uppal. Since the day of inception, Dr Rehan has been a great assistance and immense help in IDC progress and evolution. IDC’s main strength lies in use of state of the art technology, in the hands of qualified and experienced team of doctors and technologist on 24/7 basis. There is still no such setup of equivalent scale and quality in Pakistan.
IDC is one facility where both laboratory and Radiology services. The widest spectrum of in house laboratory tests and imaging investigations are available nowhere, other than at IDC. To further widen the services of rare but important tests, IDC is now offering a unique service of sending samples to UK at The Doctors Lab (TDL), and Germany, Synlab on daily basis at no extra cost.
The small and humble setup of IDC established more than decade ago is now spreaded nationwide. IDC now has a branch network of more than 2 dozen outlets and mini IDCs, with a staff of more than 300 doctors and technologist and supporting staff, working day and night to offer the best diagnostics to the patients and doctors. IDC is actively participating in external and internal quality assurance Programs from UK EQAS and USA (CAP) , NEQAP, PNRA) and ISO certification. The IDC is also involved in academic and research activities. It is affiliated with Irsa University. IDC pathologist and doctors are part of Nafees Medical College academic faculty.
IDC has the vision to provide health for all through better medical diagnostics.

IDC has taken lead in providing all type of novel studies like Real Time PCR for Hepatitis B/C and MTB, CR DR system, latest Open MRI, Digital CMOS OPG and 4D real time ultrasonography, Digital Holter Recorder & Ambulatory BP Monitor, ETT, Spirometry, Mammography, Fluoroscopy and ECHO in Rawalpindi & Islamabad tests that are not available anywhere in Pakistan are carried out in collaboration with SynLab Services (Germany) and The Doctor’s Lab (TDL) UK. Besides quality, accuracy & reliability, IDC takes pride in offering quickest turn-around times (TAT). Special cold chain shipment is provided by FedEx & DHL to meet IDC standards.
Dr. Essa’s labortary & diagnostic center founded in 1987, has rapidly achived its reputation as one of the leading laboratories in pakistan
Essa Lab specializes in a wide range of testing services available to patient’s physicians and hospitals. It pledges to provide its clients with clinical laboratory analyses that meet the required standards of quality and accuracy, using state-of-the-art equipment and methodology, thereby providing trusted & reliable results.
Prof Dr. Essa M Abdulla recently received the Eli Lilly Gold Medal 2000, presented by Prof Ata-ur-Rahman, Federal Minister of Science & Technology, for the most outstanding Microbiologist and teacher in Pakistan. The laboratory founded in 1987,when Prof. Essa returned after having a rich teaching experience for 40 years abroad.

CERTIFIED From ISO and Our organization aspires to achieve commendable standards of performance, giving physicians and patients the personal and professional commitment they expect and deserve.
In 1996, we set out to establish a medical diagnostic center that caters to the needs of patients and diagnosticians alike. Our focus has always been on providing a quality service in a timely manner. We take pride in the fact that years later, today, with a network of collection centers in and out of Lahore, AL-Nasar Lab® & Diagnostic Centre remains the provider of a wide variety of medical services for the most competitive rates in the industry. Our Mission is to provide reliable, timely, high quality, cost-effective and innovative diagnostic services & information to our patients and clients
We are only one in Lahore who provides DEXA scan, A DEXA scan is a special type of X-ray that measures bone mineral density (BMD). DEXA stands for "dual energy X-ray absorptiometry". This type of scan may also be called: a DXA scan. a bone density scan

Our quality management system is certified by TUV AUSTRIA.

Excel Lab was founded upon core values of patient priority and accurate testing. During the past 25 years we have built up a legendary reputation for excellence in both, from a small local lab we have grown to become a regional network. However, our goal remains unchanged – to serve each patient with the same care and service that is at the core of our organization.
Excel Labs utilizes state of the art equipment from top international manufacturers. In addition, the reagents used for testing are purchased directly from the authorized dealers in Pakistan to ensure that “cold chain” requirements are met. All this, along with a rigorous QC and QA program ensure that all results are of international standard.

Excel Labs is the only lab in Pakistan to have participated in the external Quality Assurance program of the College of American Pathologists for more than 20 years. By doing so, we have successfully met the CLIA standards specified for US labs

Excel Labs has also developed and implemented a quality management system that complies with the international standard ISO 9001:2008.

Al Razi Healthcare (Pvt.) Limited is a state-of-the-art private healthcare facility centrally located on M.M. Alam Road, Lahore with a focus on providing excellent hospital services supported by high quality Radiological and Laboratory diagnostics. The company operates through two main facilities; Al Razi Hospital and Al Razi Laboratory.
The hospital itself has been operational for over 5 years, providing healthcare facilities to both walk-in and corporate clients. We have over 50 foreign qualified consultants at our facility representing all major specialties such as Internal Medicine, Cardiology, Dermatology, Oncology, General Surgery, Dentistry, Palliative care etc. The hospital also offers round the clock Emergency Services and Home Services including visits from doctors and co blood sample collection obtained from the privacy and convenience of a patient’s own home – at no extra cost.
Al-Razi truly excels is in providing outstanding Radiology Services with its state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment which includes a Digital X-Ray, Dual Source 64 slice CT, and an Open bore 1.5T MRI. This equipment is by far the most highly advanced in Pakistan.




The Diagnostic Center. Aznostics private Limited is a company dedicated to providing high quality and ethical radiology and pathology diagnostics services. Established in 2011, it has in a short time developed a reputation for providing excellent consultative and investigative services and has opened satellite branches in Lahore, Gujranwala and Sialkot. We have a full range of radiology and pathology services.
We are a group of leading physicians most of whom have trained overseas and held teaching and research appointments Aznostics has a special interest in the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in particular. We hold a weekly tumor board meeting for this and are heavily involved in a charitable low cost hepatitis screening and treatment program. We are a socially responsible group and take part in many health related initiatives including blood camps, anti-smoking campaigns and hepatitis awareness.
Our laboratories are furnished with state of the art equipment and instruments, according to the most recent advancements in international laboratory and radiology industries. Combined with modern information systems, we can confidently identify our patients through digital bar-coding techniques and are able to track and monitor all tests accurately and efficiently. Our reports are available online and can be accessed from anywhere.

The combined experience of our management teams, help our clients to interact and discuss any enquiries they may have about the laboratory or radiology services provided by the Diagnostics center Network.
Working as one highly efficient team, our supporting departments are confident in providing the highest quality services throughout the Pakistan. Our clinical management teams are professional, highly qualified scientists that have vast experience in the field of medicine, clinical pathology and information technology. Such a formidable combination of scientific and managerial expertise, allow us to assist our referring doctors and clinicians.

Innova is a name of Quality and Care. We guarantee excellent facilities, provided by a team of highly qualified doctors and specialists in a very compassionate, comfortable yet professional ambiance.
With its state-of-the-art technology, Innova offers outstanding services in areas of Endocrinology, Hematology, Clinical Pathology, Molecular Biology, Microbiology and Histopathology. In addition to our diagnostic services, our esteemed clients enjoy our luxurious customers services by having an easy access to their reports via web-based reporting, free urgent reporting, SMS reporting services, WhatsApp reporting on request. Last but not the least, we also provide “Free” home sample collection services. Stay connected and enjoy our constantly evolving innovative services.

Established in 1984 in Lahore, Al-Noor Diagnostic Centre (ANDC) has been constantly facilitating the nation in the field of diagnostic services. Being a three storied building, which is situated in the heart of Lahore (Shadman), ANDC aims to provide diagnostic facilities along with other medical services under one roof. All the diagnostic facilities are supervised by the leading, highly experienced medical professionals. We guarantee quality healthcare services for your relevant medical conditions. ANDC is fully equipped with multiple high-end sophisticated ultrasound machines, 128 slice MDCT which is also capable of performing cardiac CT, MRI, fluoroscopic machine, CR system, mammography, OPG, CBCT and DEXA scan. ANDC has developed its reputation with state-of-the-art equipment and by providing outstanding, accurate / precise diagnostic services.






Citi Lab and Research Centre was established in 1986. The lab is facilitating superior quality diagnostics services to its customers through a very e!cient network of labs and collection points. We use fully automated instruments for lab tests with best accuracy and precision. This enables the lab to report test results quickly without ever compromising on quality. It is because of this reputation of uncompromising quality and quick reporting time that is the reference lab of choice for multiple hospitals and labs.
Citi lab and Research Centre has an extended nationwide network of laboratory collection centers running under strict guidelines and standard operating procedures to ensure provision of quality testing services to people all over Pakistan. An advanced patient data management system is available where test results are saved within the labs Information System, an in-house built software system, and can be easily accessed online.


At Heart, Brain, & Body Scan we are dedicated to make sure every patient’s visit is as comfortable & pleasant as possible. Our top priority is your well being. Our group of specialized & internationally recognized radiologists will provide you with the most accurate & comprehensive readings & diagnostic images utilizing state of the art equipment only found in Doctors Hospital Lahore.
We value your time and pride ourselves on offering fast, efficient, & accurate imaging and diagnosis by our internationally trained & recognized specialists.
Our radiologists are the most experienced in MRI/CT scanning in the whole country.
1st of its kind in Pakistan – we utilize advanced medical technologies & equipment only available at Heart, Brain, & Body Scan
Precise, quick , & efficient same day service – we value your time.
Picture Archive & Communication System (PACS)
The imaging services at Doctors Hospital are obtained and managed by a fully digital environment referred to as a Picture Archive and Communications System (PACS). This advanced technology means your physician can access digital images and view your test results from anywhere there is Internet access – usually within hours of your diagnostic imaging procedure. The PACS system enables healthcare providers to get vital imaging results and information about your health faster so that treatment of your medical concerns can happen even more quickly.
Toshiba ELAN 1.5 Tesla MRI
Our Toshiba Elan 1.5 TESLA MRI offers unparalleled MRI imaging utilizing the latest medical technologies while providing ultra fast scanning – all to save you time. This machine is utilized in multiple cases including MRI of the brain, spine, joints, pelvis, abdomen, MRCP, face & neck and more.
Toshiba Aquilion 64 Slice CT Scan
Our Toshiba Acquilion 64 slice CT scan machine offers unparalleled imaging and diagnosis. Most exams are completed in less than 1 minute on the machine table offering extremely fast service & accurate results.
The 64-slice CT scanner is even more powerful than a regular CT scanner in that it captures up to 64 simultaneous anatomical slices of 0.5 mm in a single gantry rotation. Even precise images of rapidly moving organs like the heart and lungs are possible. It is also proving revolutionary in helping examine patients who can’t hold their breath, such as trauma victims, young children or the extremely ill.
Two Open-bore MRI machines
The completely open bore architecture of this machine is ideal for larger patients and patients who are claustrophobic.
The MRI machine with “larger bore” has a larger opening than traditional MRI machines, making it easier for patients who are claustrophobic to have MRI scans, without sedation. In contrast to a “completely open” MRI machine it still has a tunnel the patient must pass through, but the opening (or “bore”) is wider and much shorter. The patient having their spine or pelvis examined will rest with their head and lower extremities outside the magnet.
This has a most powerful magnet giving us clearer pictures in a much shorter time. Most examinations are completed in 10-12 minutes.
Complete Nuclear Medicine – Diagnostic and Therapeutic
Nuclear medicine is a branch of medical imaging that uses small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose and determine the severity of or treat a variety of diseases, including many types of cancers, heart disease, gastrointestinal, endocrine, neurological disorders and other abnormalities within the body. Because nuclear medicine procedures are able to pinpoint molecular activity within the body, they offer the potential to identify disease in its earliest stages as well as a patient’s immediate response to therapeutic interventions.
Nuclear medicine imaging procedures are noninvasive and, with the exception of intravenous injections, are usually painless medical tests that help physicians diagnose and evaluate medical conditions. These imaging scans use radioactive materials called radiopharmaceuticals or radiotracers.

Punjab Clinic of Radiology is a diagnostic set-up providing par excellence radiological services for more than two decades with multi-modality imaging as its mainstay.
Our motto is to provide high-quality, affordable diagnostic services under one roof. The clinic is equipped with latest, state of the art diagnostic equipment run by trained staff and interpreted by a team of qualified and experienced radiologists under the supervision of Dr. Tanveer Zubairi, Chief consultant radiologist, Services hospital, Lahore.
5-D Ultrasound
We specialize in providing high end ultrasound services, using top quality equipment. We provide
Siemens Open MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic test that uses a magnetic field and pulses of radio wave energy to make pictures of organs and structures that are inside the body.
We offer open MRI services with high quality image results and no risk of claustrophobia. We also provide prompt, same day reporting for emergency cases.
CT Scan
A computerized tomography (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images, or slices, of the bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside your body.
We offer multi-detector modern 3D scan imaging at affordable rates.

To make use of best diagnostic testing services and delivering them at doorsteps of patients, doctors and healthcare service providers. To offer the “BEST ADVANCED CARE” through our core values of excellence, reliability, punctuality, novelty, safety, accuracy and sincerity. We work on the philosophy of “PATIENT HEALTH & WELLNESS FIRST”
Chairman Message (Dr Zahid Asgher)
WE, at Doctors Diagnostic Centre, started our journey with the responsibility of creating centre of brilliance providing the utmost quality of Medical Diagnostics to the patients
VISION & MISSION
Accreditations:
National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of Pakistan accreditation has been applied for. We are also external quality assurance participant in Pakistan, Lahore/ Voluntary inter laboratory Analytical Comparison (VILAC). EQAS External Quality Assurance Scheme (Bio-Rad) For Both CHEMISTRY /IMMUNOASSAYS. CMC Vellore External Quality Assessment Scheme.

Lab one was incorporated in the year 2003 by Prof. Dr. Javed Asif and Mr. Mumtaz Khan. Since then Lab One continued to facilitate patient care by providing high quality, cost effective and certified laboratory testing to patients and referring centers all over Pakistan. Lab One is one of the leading state-of the-art laboratory in Lahore and serves a critical role in the health care perpetuity. We offer reliable test and efficient delivery of reports providing quality health care. Lab One aims not to earn but to serve the patients with its best resources and abilities.


In keeping with our tradition of being pioneers in our field, we are pleased to announce the induction for the first time in Pakistan, of the latest and state of the art Fresenius 5008 machines in our Lahore center. These machines provide superior quality dialysis with least complications with exceptional patient satisfaction